Removable And Nonremovable Discontinuity / 1 4 Continuity And One Sided Limits This Will Test The Limits Of Your Brain Ppt Download - Type removable (r) or nonremovable (nr) if r, what values makes it continuous?
Removable And Nonremovable Discontinuity / 1 4 Continuity And One Sided Limits This Will Test The Limits Of Your Brain Ppt Download - Type removable (r) or nonremovable (nr) if r, what values makes it continuous?. Is is possible to have a function with a removable and nonremovable discontinuity? Points of discontinuity are also called removable discontinuities and include functions that are undefined and appear as a hole or break in the graph. Transcribed image text from this question. Introduction to removable and nonremovable discontinuities a complete introduction with definitions, examples, and the intuition. The graph of a removable discontinuity leaves you feeling empty, whereas a graph of a non removable discontinuity leaves you feeling jumpy.if a term doesn't cancel ,the discontinuity at this x value corresponding to this term for which the denominator is zero is nonremovable.
Find the value of k that makes the function continuous. Removable and nonremovable discontinuities describe the difference between a discontinuity that is removable and a discontinuity that is nonremovable. That is, a discontinuity that can be repaired by filling in a single point. Removable or nonremovable discontinuity example with absolute value. All discontinuity points are divided into discontinuities of the first and second kind.
Then give an example of a function that satisfies each description.
All discontinuity points are divided into discontinuities of the first and second kind. If #f# has a discontinuity at #a#, but #lim_(xrarra)f(x)# exists, then #f# has a removable discontinuity. Explain how any removable discontinuities should be defined or redefined to make the function continuous. That is, a discontinuity that can be repaired by filling in a single point. A function is said to be discontinuous at a point when there is a gap in the. I will always take a removable battery phone over a nonremovable battery phone. Click on the graph either to the left or to the right of the removable discontinuity (hole). The graph of a removable discontinuity leaves you feeling empty, whereas a graph of a non removable discontinuity leaves you feeling jumpy.if a term doesn't cancel ,the discontinuity at this x value corresponding to this term for which the denominator is zero is nonremovable. A hole in a graph. Then give an example of a function that satisfies each description. Answer 1) a removable discontinuity is basically a hole in a graph whereas. This discontinuity causes a vertical. Such a point is called a removable discontinuity.
Continuity basic introduction, point, infinite, & jump discontinuity, removable & nonremovable. Such a point is called a removable discontinuity. Which of the discontinuities are removable? So, one example function that contains both kinds of discontinuity, is: Explain how any removable discontinuities should be defined or redefined to make the function continuous.
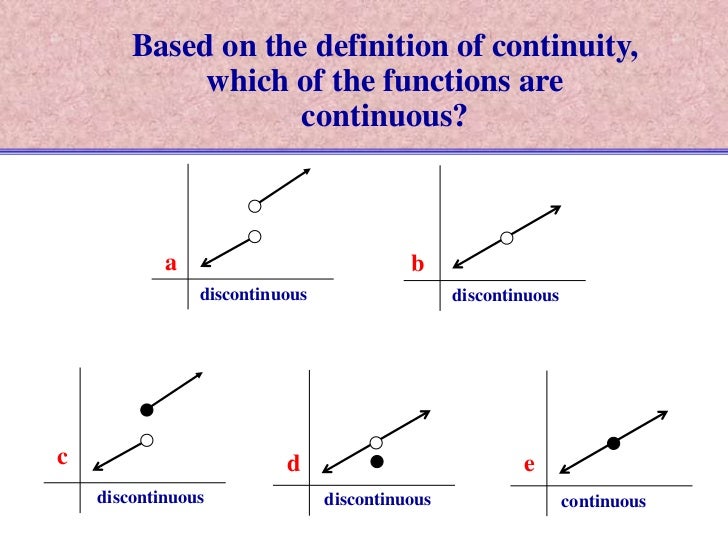
Which we call as, removable discontinuity.
Click on the graph either to the left or to the right of the removable discontinuity (hole). There are two ways a removable discontinuity can be created. The first way that a function can fail to be continuous at a point a is that. Transcribed image text from this question. Question 1) what is the difference between removable and nonremovable discontinuity? Infinite and jump discontinuities are nonremovable discontinuities. There is a small open circle at the point where x=2.5. Is there a paper or site that i can see how this is possible or understand this better? If #f# has a discontinuity at #a#, but #lim_(xrarra)f(x)# exists, then #f# has a removable discontinuity. (a) a function with a nonremovable discontinuity at x = 4 (b) a function. Removable and nonremovable discontinuities describe the difference between a discontinuity that is removable and a discontinuity that is nonremovable. The following function factors as shown: A point discontinuity is a hole also known as a removable discontinuity.
Explain how any removable discontinuities should be defined or redefined to make the function continuous. Here is an example that shows both kinds. (a) a function with a nonremovable discontinuity at r = 4. Infinite and jump discontinuities are nonremovable discontinuities. Which of the discontinuities are removable?

Removable and nonremovable discontinuities in exercises 41.
Removable or nonremovable discontinuity example with absolute value. A removable discontinuity is the subtraction of a point. There is also jump discontinuity. (a) a function with a nonremovable discontinuity at x = 4 (b) a function. Which of the discontinuities are removable? Here is an example that shows both kinds. A function is said to be discontinuous at a point when there is a gap in the. Which we call as, removable discontinuity. That is, a discontinuity that can be repaired by filling in a single point. 02.02.2021 · removable and nonremovable discontinuities describe the difference between a discontinuity that is removable and a discontinuity that is nonremovable. The graph of $$f(x)$$ below shows a function that is discontinuous at $$x = a$$. All discontinuity points are divided into discontinuities of the first and second kind. There is a small open circle at the point where x=2.5.
Komentar
Posting Komentar